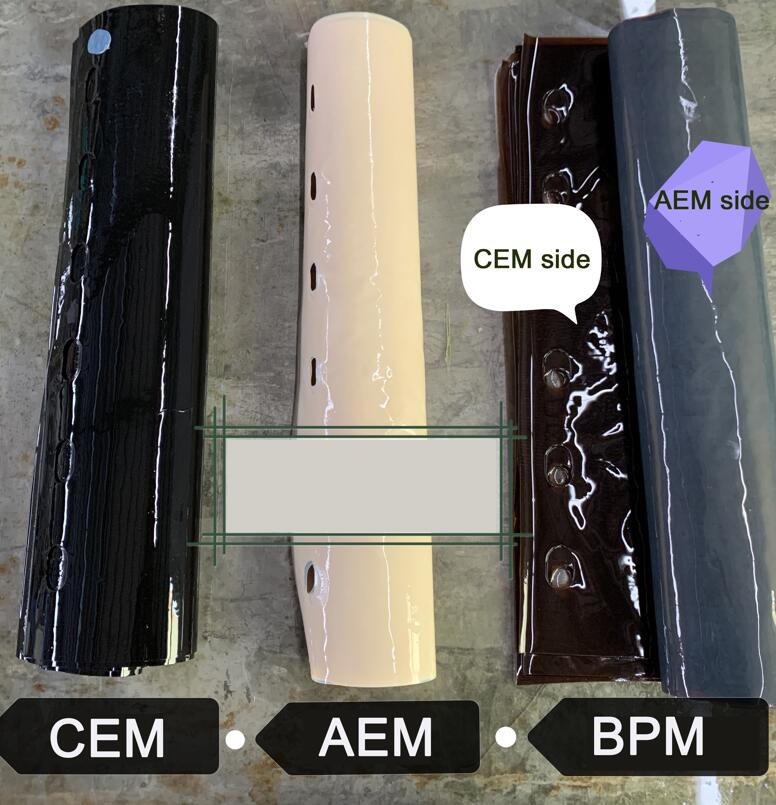
About
Bipolar Membrane BPM
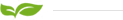
A bipolar membrane is an ion exchange membrane with positively charged groups on one side of the membrane and negatively charged groups on the other side. The bipolar membrane can be divided into three layers in the spatial structure, namely the cathode layer (with immobilized positive charge groups, which is equivalent to an anion exchange membrane), the catalytic layer (catalyzes the hydrolysis reaction) and the anode layer (with immobilized negative charges,equivalent to cation exchange membrane). Under the action of the reverse DC electric field of the bipolar membrane, the H2O molecules in the catalytic layer dissociate into H+ and OH- under the action of the catalyst, and then migrate to the main solution on both sides of the membrane through the anode and cathode layers respectively. The decrease in the concentration of H+ and OH- in the catalytic layer makes the hydrolysis reaction continue. The bipolar membrane is equivalent to a hydrolysis generator that produces H+ and OH- ions.
Taking sodium sulfate using bipolar membrane to prepare acid and alkali as an example, when sodium sulfate enters the salt chamber, under the action of a direct current electric field, sulfate ions migrate through the negative membrane to the acid chamber, and encounter the positive membrane surface of the bipolar membrane. The surface is negatively charged, so sulfate ions cannot continue to migrate and stay in the acid chamber to combine with the hydrogen ions decomposed on the positive membrane surface of the bipolar membrane to form sulfuric acid. Under the action of a direct current electric field, the negative membrane surface of the bipolar membrane continuously decomposes hydroxide ions, which combine with sodium ions in the alkali chamber to generate sodium hydroxide. Finally, sodium sulfate is converted into sulfuric acid and sodium hydroxide through bipolar membrane electrodialysis. The details are shown in the figure: