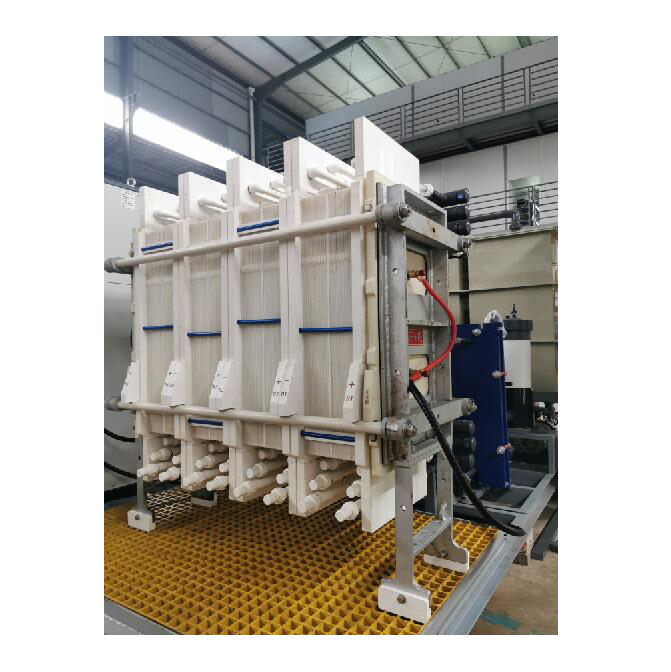
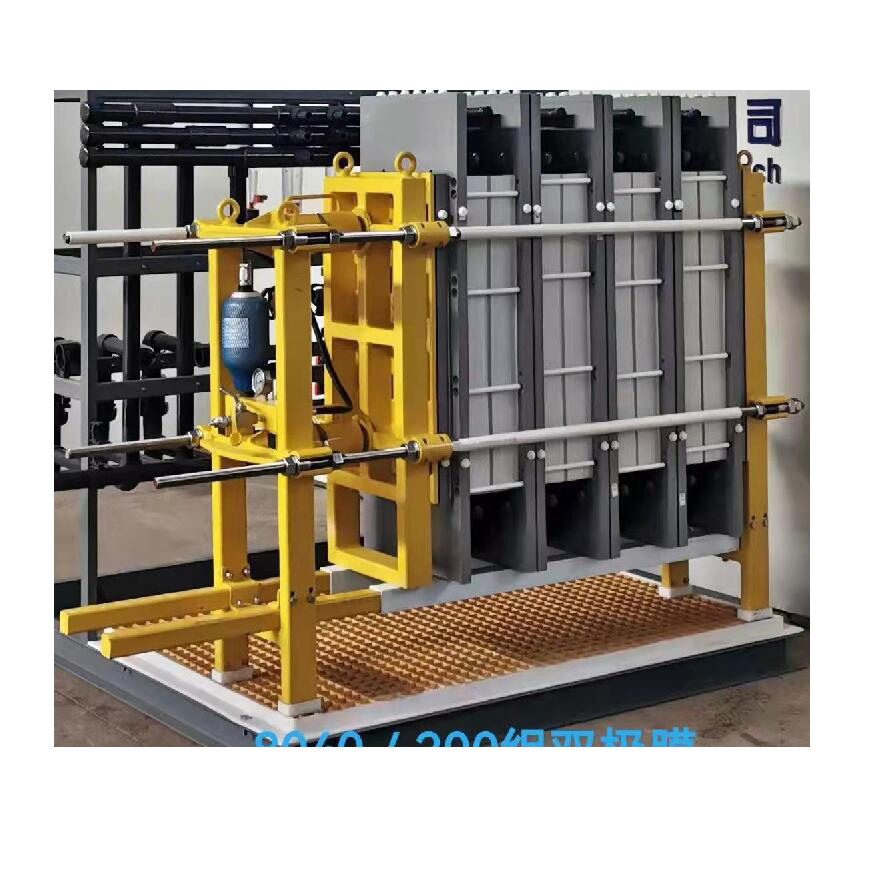
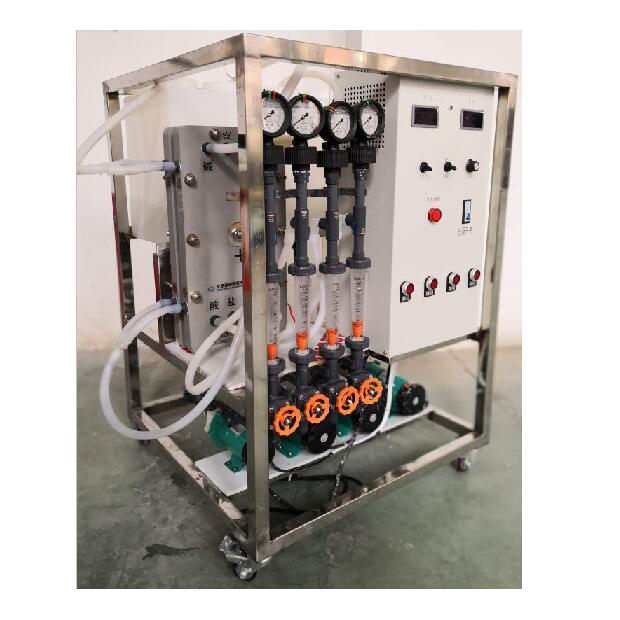
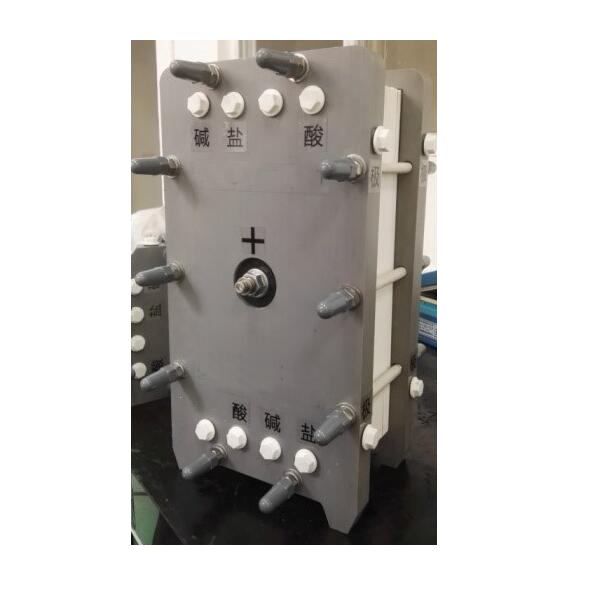
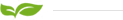Chemical Name: Membrane Electrodialyser
Principle of electrodialysis
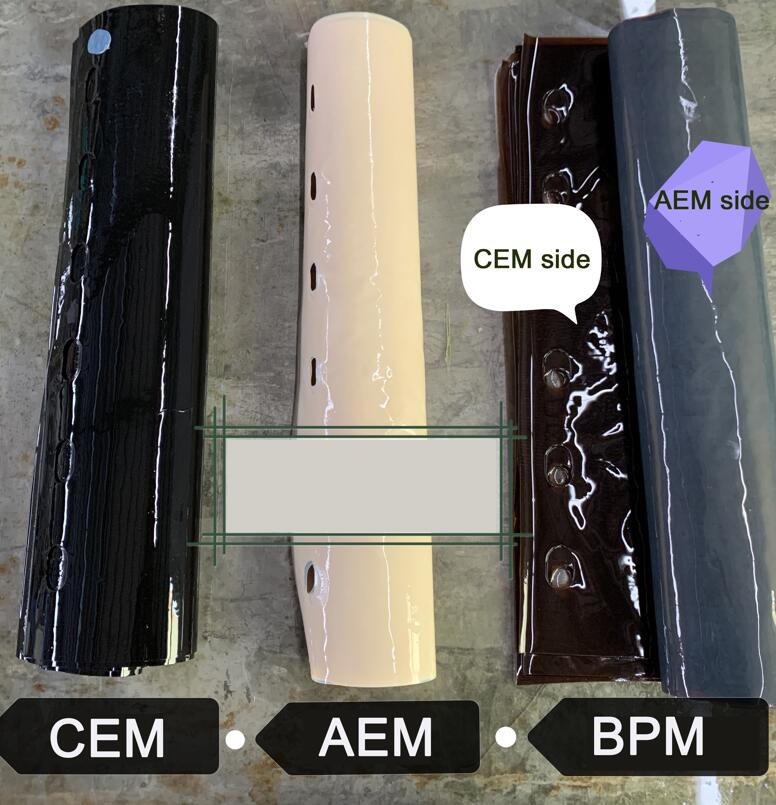
The semi-permeable membranes used in electrodialysis are ion exchange membranes. This ion exchange membrane is divided into two types: cation exchange membrane and anion exchange membrane. In an aqueous electrolyte solution, the cationic membrane allows the permeation of cations and repels and blocks the anions, and the anion membrane allows the permeation of anions and repels and blocks the cations, which is the selective permeability of the ion-exchange membrane. In the process of electrodialysis, the ion exchange membrane only plays a selective permeation effect on ions of different electrical properties. The compartment composed of electrodes and membranes in the electrodialysis process is called the electrode chamber. The oxidation reaction occurs in the anode chamber, the anode water is acidic, and the reduction reaction occurs in the cathode chamber, and the cathode water is alkaline.
Electrodialysis can be said to be a desalination technology, because all kinds of water (including natural water, tap water, industrial wastewater) have a certain amount of salt, and the anions and cations that make up these salts will be separated under the action of a DC electric field. Move the electrode in the opposite direction. If an anion and a cation exchange membrane are inserted into an electrodialyser, due to the selective permeability of the ion exchange membrane, that is, the cation exchange membrane only allows cations to pass freely, and the anion exchange membrane only allows anions to pass through. In the middle compartment, the concentration of salt will decrease due to the directional migration of ions, while the two compartments near the electrode are the concentration chambers for anion and cation, and finally the desalination chamber in the middle achieves the purpose of desalination.
Synonyms: Membrane Electrodialyser, Membrane Electrodialyzer, Ion Exchange Membrane Electrodialyser, Membrane Electrodialysis Stack,Ion Exchange Membrane Electrodialysis Stack, Electroosmosis
Application:Brackish water desalination, concentration and desalination
Month Capacity:300 pieces
Electrodialyser Type:
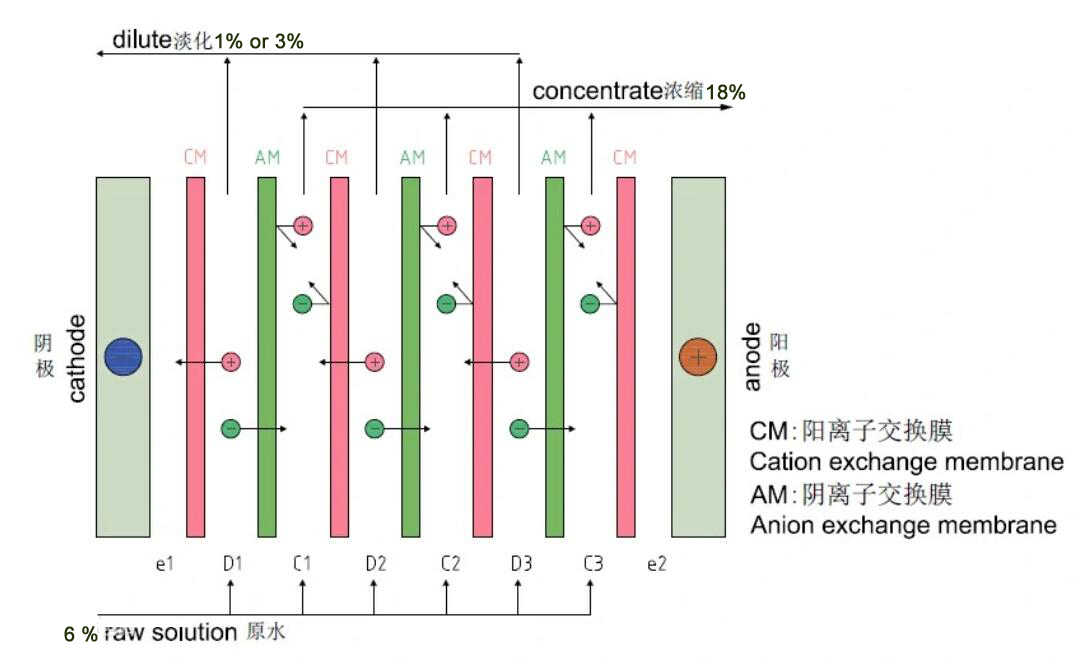
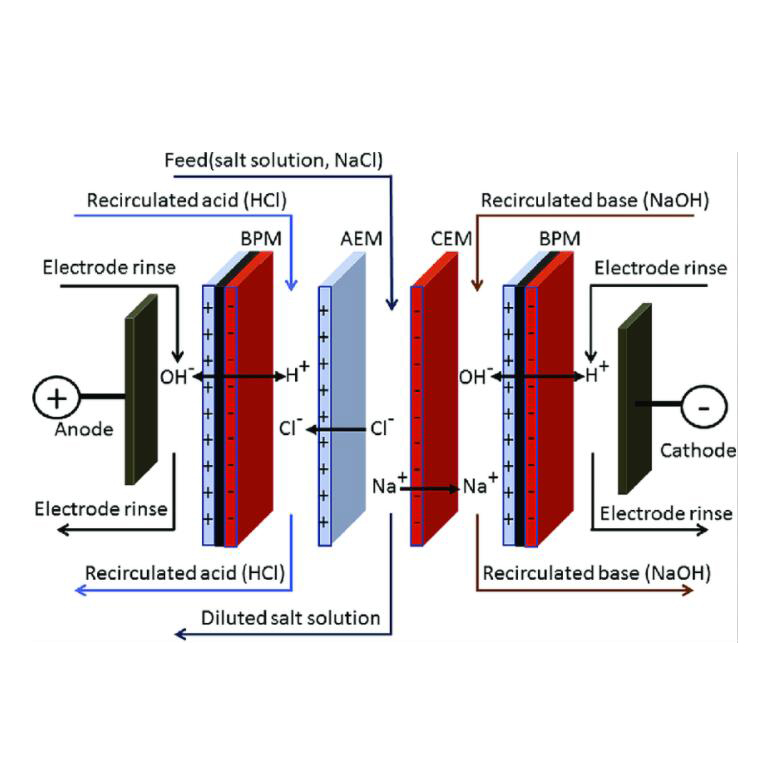
1,bipolar membrane electrodialysis BPED
The MBED process is a unique electrodialysis process. It is usually formed by superimposing cation and anion exchange membranes together. The channels of these two membranes constitute a water-containing intermediate layer. Under the action of an electric field, the possible ions are first migrated out of the intermediate layer, and then dissociated through the water. It acts on the negative and positive sides of the membrane to generate H+ ions and OH- ions, respectively. Its biggest feature is that it can be cleverly combined with other anion exchange membranes and cation exchange membranes to form many unique bipolar membrane electrodialysis processes. Compared with the electrolytic dehydration method, the energy consumption is greatly reduced, and equimolar acid and alkali can be generated from the salt solution, so this technology can be used for the regeneration and utilization of waste acid, waste alkali and other substances, reducing the consumption of materials and energy, reducing Waste discharge, eliminate environmental pollution and provide new ways for the separation and preparation of certain acids and bases
2,Inverted Electrodialysis EDR
The EDR process refers to switching the polarity of the positive and negative electrodes at regular intervals (usually 15-20min) (frequently reversed), which can automatically clean the ion-exchange membrane and the dirt on the surface of the electrodes to ensure the quality and quantity of fresh water, and the ion-exchange membrane. Stable operation and minimum concentrated water discharge, EDR system is composed of three parts: electrodialysis body, rectifier and automatic reverse pole system. The pole reverse operation procedure is as follows:
1. Change the polarity of the DC power supply electrode, so that the thick and thin chambers are interchanged, and the ion flow is reversed;
2. Change the water inlet and outlet valves, so that the water supply and drainage systems of the thick and thin chambers can be interchanged;
3. Continue 1-2 minutes after the polarity change, put the unqualified fresh water into the concentrated water system, and then the concentrated and fresh water will go their separate ways and resume normal operation.
2,Packed Bed Electrodialysis EDI
Packed bed electrodialysis, also known as ionization method, is a new type of water treatment technology that organically combines ion exchange membrane and ion exchange resin to remove ionized or ionizable substances in water under the action of a DC electric field. . It utilizes the polarization phenomenon in the electrodialysis process to electrochemically regenerate the ion-exchange packed bed. It cleverly concentrates the advantages of the two methods of continuous desalination by electrodialysis and deep desalination of ion-exchange resins, and overcomes their disadvantages, namely, electrodialysis. Concentration polarization phenomenon of dialysis process and chemical regeneration process of ion exchange. Generally, it can be used when the salt content in water is (50-15000mg/L), but it is more suitable for water with low salt content. This method can basically remove all ions in water, so it has a wide range of uses in the preparation of high-purity water and the treatment of radioactive wastewater
Applications Areas:
1, Preparation of acid and bases from inorganic salts (such as sodium sulfate, sodium chloride, lithium chloride, etc.)
2, Production of organic acids (such as gluconic acid, lactic acid, malic acid, succinic acid, etc.)
3, Production of organic bases (such as ornithine, lysine, arginine, histidine, etc.)
Applications Cases:
1,Treatment and recycling of saline wastewater
2,Direct production of hydrochloric acid and sodium hydroxide from table salt (sodium chloride) Direct production of vitamin C from sodium salt of vitamin C
3,Direct production of tartaric acid from sodium tartrate
4,Direct production of lactic acid from sodium lactate
5,Direct production of gluconic acid from sodium gluconate
6,Direct production of methanesulfonic acid from sodium methanesulfonate
7,Direct separation of amino acids from fermentation broth
8,Recovery of acetic acid from sodium acetate waste water
9. Electrodialysis is used for desalination and desalination of water, concentration of seawater for salt production, refined dairy products, deacidification and purification of fruit juice, preparation of chemical products, etc.
10. Electrodialysis can be used for the pretreatment of high-purity water produced in food, light industry and other industries to produce pure water, electronics, medicine and other industries.
11. Electrodialysis can be used for primary softening and desalination of boiler feed water, and desalination of brackish water into drinking water.
12. The electrodialyzer is suitable for water supply treatment in electronics, medicine, chemical industry, thermal power generation, food, beer, beverage, printing and dyeing and coating industries. It can also be used in physical and chemical processes such as concentration, purification and separation of materials.
13. Electrodialysis can also be used for the treatment of waste water and waste liquid and the recovery of precious metals, such as the recovery of nickel from electroplating waste liquid.