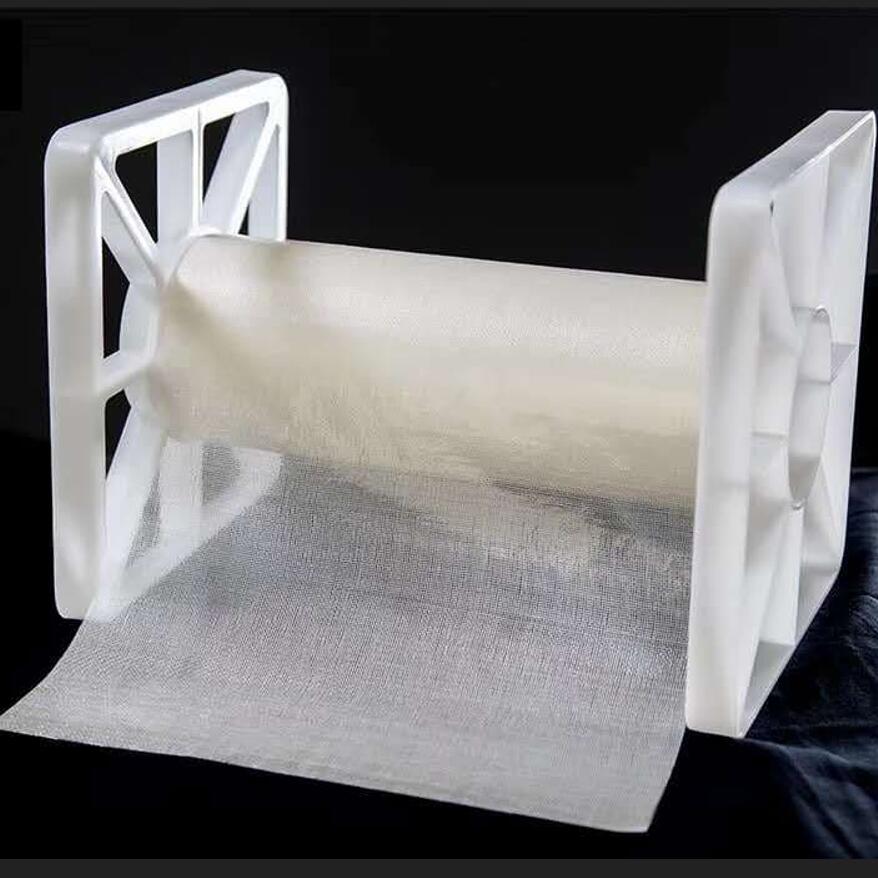
Chemical Name:Perfluorinated ion exchange membrane N-31
Synonyms:Perfluorinated proton exchange membrane,perfluorinated ionomer membrane,proton exchange membrane,ion exchange membrane,Perfluorosulfonic acid membrane
CAS NO.:31175-20-9
Appearance: White membrane
Formula:(C7HF13O5S . C2F4)x
Application:hydrogen fuel cell,vanadium flow batteries, chlor-alkali industry for the production of NaOH and KOH, water treatment device
REF. FOB Price:USD100-500/Piece
Min. Order:1 piece
Payment Terms:L/C,T/T,Western Union,Paypal
Lead Time:10-15 days
Month Capacity:30000 square meters
Technical Index:
Physical and Other Properties
Physical Properties
Measured at 50% RH, 23 C |
Values |
Test Method |
|
|
|
Tensile Strength MD, max., MPa |
36 |
ASTM D882 |
Tensile Module, MPa |
410 |
ASTM D882 |
Elongation at break, % |
190 |
ASTM D882 |
Specific Gravity |
1.98 |
|
|
|
|
Other Properties |
Values |
Test Method |
Conductivity, S/cm |
0.10 |
GB/T 20042.3-2009 |
Acid capacity, meq/g |
1.0 |
GB/T 20042.3-2009 |
|
|
|
Hydrolytic Properties |
Values |
Test Method |
Water Content, % |
5.0+-3.0 |
ASTMD570 |
Water Uptake, % |
50.0+-5.0 |
ASTMD570 |
Thickness Change,
from 50% RH, 23 C to water soaked, 23 C
from 50% RH, 23 C to water soaked, 100 C |
10.0%
18.0%
|
ASTM D 756
ASTM D 756 |
Linear Expansion,
from 50% RH, 23 C to water soaked, 23 C
from 50% RH, 23 C to water soaked, 100 C |
10.0%
15.0%
|
ASTM D 756
ASTM D 756 |
1, Measurements taken with membrane conditioned to 23 C,50% RH.
2, Conductivity measurements at 23 C,100% RH.
3, A base titration procedure measures the equivalents of sulfonic acid in the polymer, and uses the measurement to calculate the acid capacity or equivalent weight of the membrane.
4, Water content of membrane conditioned to 23 C and 50% RH (dry weight basis).
5, Water uptake from dry membrane to conditioned in water at 100 C for 1hour (dry weight basis ).
Thickness of the PFSA membranes
Type |
Thickness(um) |
N-31 |
N-310 |
10 |
N-312 |
12 |
N-315 |
15 |
Application:
The PFSA membranes N-31 are non-reinforced films based on PFSA polymer, a perfluorosulfonic acid in the acid (H+) form. Our PFSA membranes perform as a solid polymer electrolyte in fuel cells and other applications in electrochemistry and separation technology for a variety of electrochemical process.
The membranes are located between the cathode and anode and transports protons formed near the catalyst at the hydrogen electrode to the oxygen electrode thereby allowing the current to be drawn from the cell. The membranes show significant improvements in features such as better resistance to chemical attack and longer operating durability.