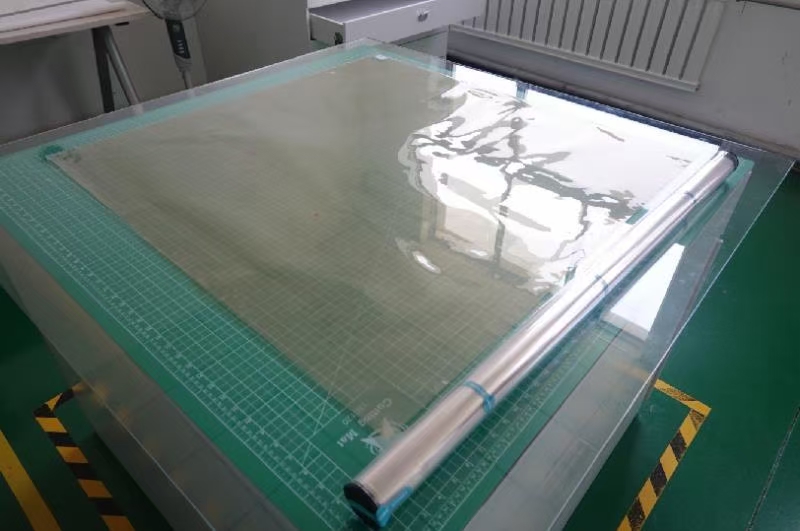
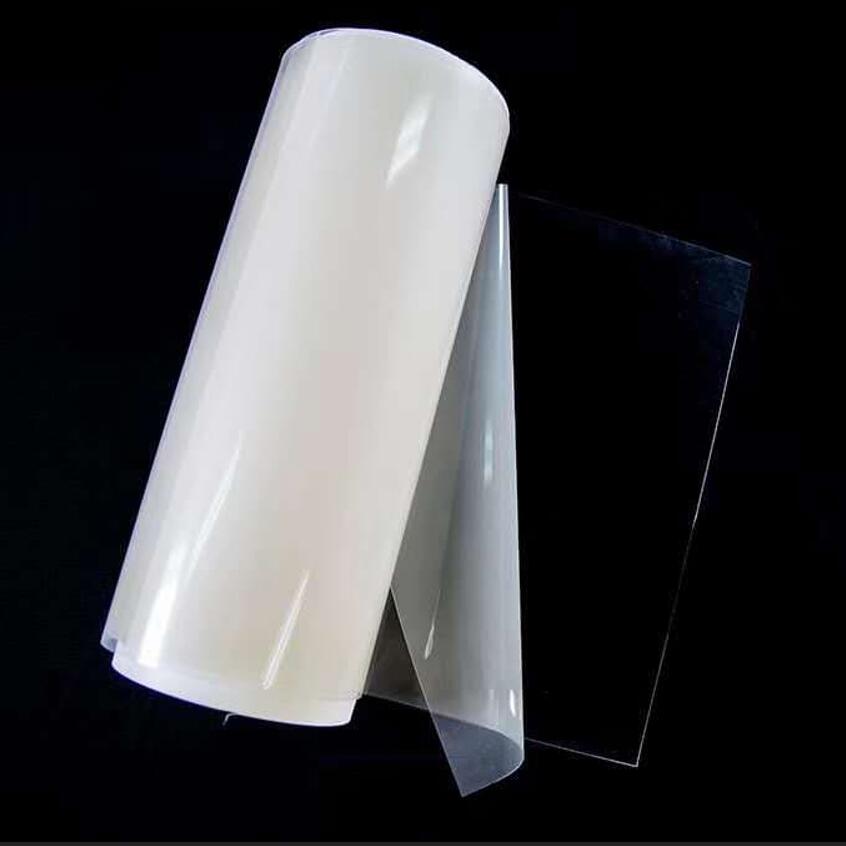
About
Perfluorosulfonic Acid Ion Exchange Membrane for Fuel Cell
Fuel Cell ion exchange membrane, also known as perfluorosulfonic acid proton exchange membrane and cation exchange membrane, is a solid polymer electrolyte, a strong acid type ion exchange membrane, with good chemical and thermal stability, low voltage, and low membrane resistance. High conductivity, good hydrophilicity, high water content of the membrane, high mechanical strength, etc., it can can be used under harsh conditions such as strong acid, strong alkali, strong oxidant medium and high temperature. Due to its own characteristics, perfluorosulfonic acid Proton exchange membranes are used as key components of proton exchange membrane fuel cells.
The fuel cell is a type of power generation device. The working principle of a fuel cell is that the battery contains two electrodes, cathode, and anode, which are filled with electrolytes, and the two electrodes are formed by a permeable ion exchange membrane. Hydrogen enters the anode (negative electrode) of the fuel cell, and oxygen enters the fuel cell from the cathode. Through the action of the catalyst, the hydrogen molecules of the anode are decomposed into two protons and two electrons. The protons are 'attracted' by the oxygen to the other side of the ion exchange membrane. Under the action of the catalyst, protons, oxygen, and electrons react to form water molecules, so water can be said to be the only emissions from fuel cells. Since the oxygen supplied to the cathode plate can be obtained from the air, as long as the anode is continuously supplied with hydrogen, the cathode is supplied with oxygen, and the water is taken away in time, the electrical energy can be continuously provided.